Electric vehicle involves at least one electric motor for propulsion. It very well may be controlled by a gatherer framework, with power from external sources, or it tends to be controlled independently by a battery (charged by sun-powered chargers, or by changing fuel over completely to power utilizing energy units or a generator).
Electric vehicles previously appeared during the nineteenth hundred years, when power was among the favored strategies for vehicle drive, giving a degree of solace and simplicity of activity that couldn’t be accomplished by the gas vehicles of the time. Gas-powered motors were the predominant drive strategy for vehicles and trucks for around 100 years, yet electric power stayed typical in other vehicle types, like trains and more modest vehicles, everything being equal.
Types of Electric Vehicle
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEVs)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEVs)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEVs)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEVs)
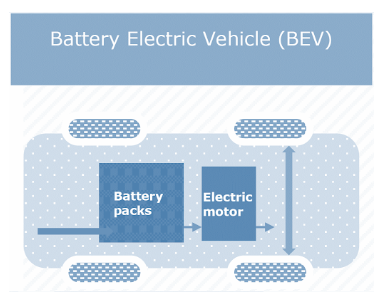
1. Battery Electric Vehicle: Battery electric vehicle (BEVs) is also known as all-electric vehicle. BEV for propulsion purely depends on the battery without any source of energy (eg. Hydrogen fuel cell, IC Engine). Battery charged by an external source of electricity. Instead of IC Engine BEVs uses an electric motor to propel the wheels. An electric motor may be Alternating Current (AC) or Direct Motor (DC). The type and size of the motor purely depend on the working load and conditions. A hybrid vehicle whose batteries can be charged externally is known as a plug-in hybrid vehicle. The idea of battery electric vehicles is to involve charged batteries on board vehicles for inputs. Battery electric vehicles are turning out to be increasingly more alluring with the higher oil costs and the headway of new battery innovation (lithium-particle) that have higher power and energy thickness compared to more established battery types like lead-corrosive batteries.
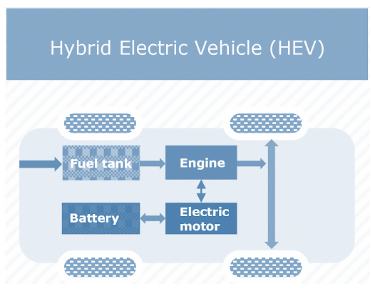
2. Hybrid Electric Vehicle: Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) use more than one power source for propulsion. Hybrid electric vehicles run on fossil energy or Electric energy or a combination of both fossil and electric energy. Due to combinations of both energies HEVs cannot be considered pure and all-electric vehicles. The presence of an electric powertrain is intended to achieve better fuel economy.
2.1 Series HEV
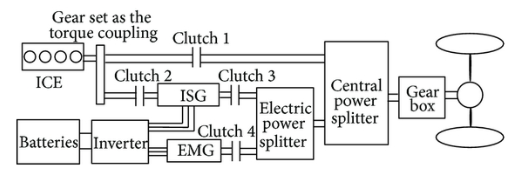
In a series hybrid, only the electric motor drives the drivetrain and a small IC engine (also called range extender) works as a generator to power the electric motor or to recharge the batteries. They also usually have a large battery pack than the parallel hybrid, making it more costly. Once the battery is low the small IC engine is used to recharge the batteries. As indicated by Hybrid Center, the structure of equal half breeds makes them more productive for thruway driving at higher, more consistent velocities. On the other hand, series half breeds are more productive for driving in the city because their drivetrain structure decreases the burden on the motor in unpredictable driving circumstances.
2.2 Parallel HEV
In a parallel hybrid, the IC engine and the electric motor both are connected to the mechanical transmission and can simultaneously transmit power to drive the wheels. In most Parallel HEV electric motors and gearbox are connected through automatic clutches. Parallel HEV can be propelled as a pure electric tractor. For pure electric mode, the clutch between the power drive and wheels is disengaged. To prople vehicle as a parallel hybrid in high mode clutch will be engaged.
2.3 Power split HEV
Power split hybrid has both the characteristics of Series hybrid and Parallel hybrid. In split HEV power will be transferred in both manner series as well as parallel. Initial cost of a power-split HEV is more than that compared to series and parallel HEV. Working efficiency of the power-split hybrid is better than series and parallel hybrid in rural areas. Ex. – 2007 model of Lexus.
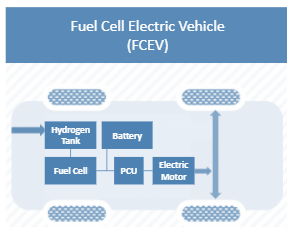
3.Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle: FCEVs are also called Zero-Emission Vehicles. They utilize ‘energy unit innovation’ to create the power expected to run the vehicle. The substance energy of the fuel is changed into electric energy. Power devices in vehicles produce power for the most part utilizing oxygen from the air and packed hydrogen. Most power device vehicles are delegated zero-discharges vehicles that produce just water and intensity. As contrasted and inner ignition vehicles, hydrogen vehicles incorporate toxins at the site of the hydrogen creation, where hydrogen is normally gotten from changed flammable gas. Moving and putting away hydrogen may likewise make contaminations.
4.Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs): A module cross breed electric vehicle (PHEVs) is a half and half electric vehicle whose battery pack can be re-energized by stopping a charging link into an outside electric power source, notwithstanding inside by its ready gas-powered motor fueled generator. Most PHEVs are travelers vehicles, however, there are additionally PHEVs adaptations of business vehicles and vans, utility trucks, transports, trains, bikes, mopeds, and, surprisingly, military vehicles. Like every single electric vehicle (BEVs), PHEVs dislodge ozone-depleting substance discharges from the vehicle tailpipe exhaust to the power station generators fuelling the power matrix. These brought-together generators might be of sustainable power (for example sunlight-based, wind, or hydroelectric) and to a great extent outflow free, or have a generally lower emanation force than individual gas-powered motors. Contrasted with traditional mixture electric vehicles (HEVs), PHEVs have a bigger battery pack that can be charged from the power lattice, which is likewise more proficient and can cost not as much as utilizing just the on-board generator, and further more frequently have an all the more remarkable electric result able to do longer and more continuous EVs mode driving, assisting with lessening working expenses. A PHEV’s battery pack is more modest than all-electric vehicles for similar vehicle weight, yet has the helper choice of changing back to utilizing its gas/diesel motor like a customary HEVs on the off chance that the battery runs short, mitigating range uneasiness, particularly for places that need the adequate charging framework.
Advantages of Electric Vehicle over Fossil fuel vehicle
- Cleaner environment.
- No congestion charges.
- Lower running costs.
- Renewable electricity tariffs.
- Better driving experience.
- Government funding.
- Reduced noise pollution.
- Environmentally friendly as they do not emit pollutants.
- Lower maintenance due to an efficient electric motor.
- Better Performance.
Electric vehicles (EVs) offer a chance to supplant non-renewable energy sources in the vehicle area. Electrification of the transport sector can also bring benefits in terms of increased energy efficiency and reduced local pollution. In a recent survey, we found that electric vehicles could displace oil demand of 2 million barrels a day as early as 2023. That would create a glut of oil equivalent to what triggered the 2014 oil crisis. Compound annual growth rates as high as 60 percent can’t hold up for long, so it’s a very aggressive forecast.
By Rohit Malik | July 10, 2022
B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering)
Alumni of Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, Patiala, Punjab, India.







Recent Comments