Cellular Agriculture: An Answer to Growing Food Demand?
Cellular Agriculture: It’s Time To Farm Cells, Not Animals
To fulfill the demand for products like dairy, leather, and meat, animal farming is being practiced globally for over decades. Being the most positive and nutritional for society, they are now proving to be more destructive because of increasing allergic responses to the consumers. Earlier people were dependent on animals for their need for agricultural products but now humanity has experimented with a lot of means to replace this necessity with a novel approach called “cellular agriculture”.
The Key Concept behind Cellular Agriculture
Cellular Agriculture is defined as a concept of farming that produces animal-based products without the need of rearing and raising animals on the farm. This is not only beneficial for human health but also addresses the issues of environment and animal rights. Therefore, it now has the potential to revolutionize the world which was earlier dependent on animal farming. This technique of creating animal-based products is poised to fulfill the growing demands of precision nutrition with the least impact on the environment.
How Does It Work?
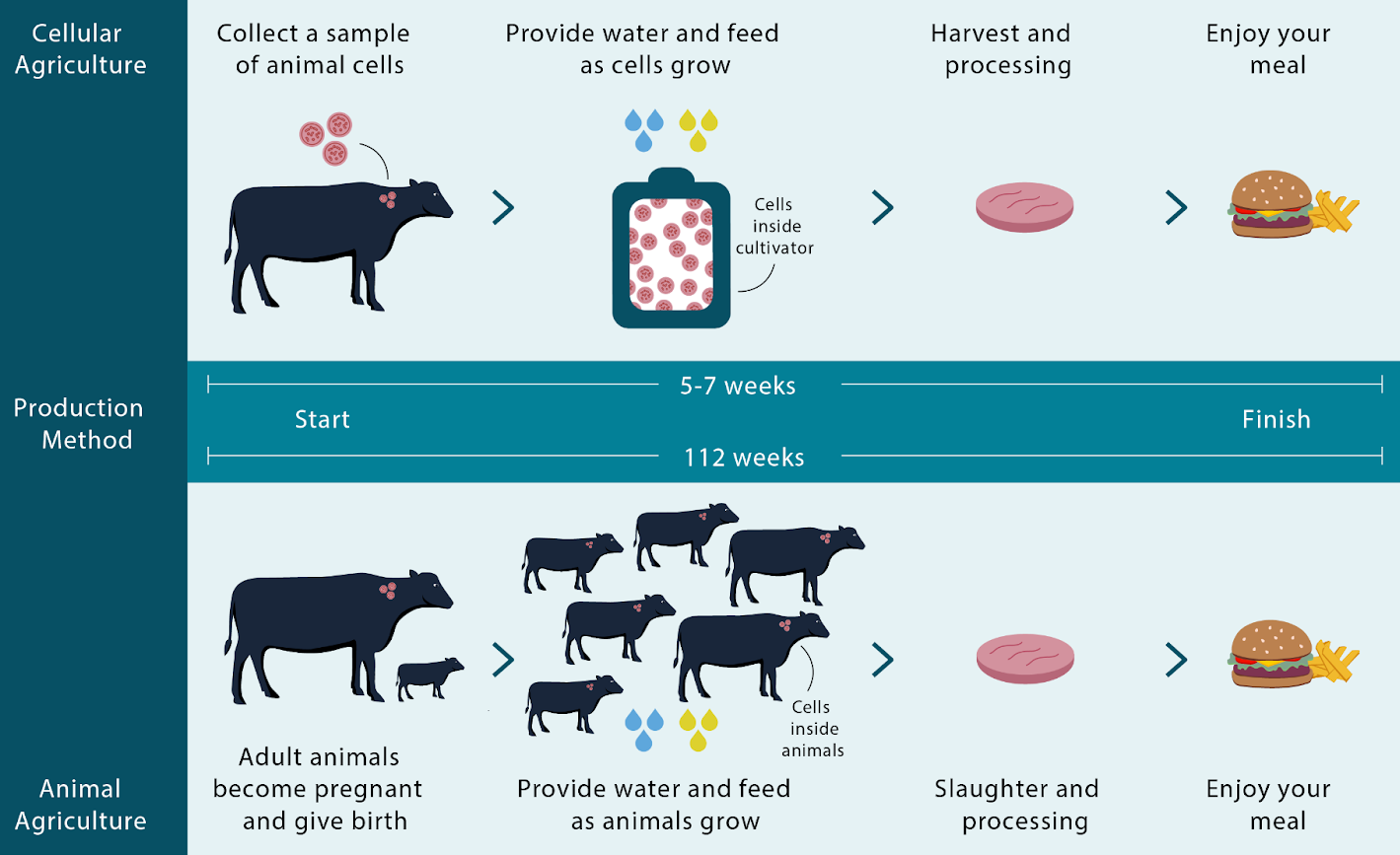
The cellular agriculture technique makes use of individual cells from animals, plants, or unicellular organisms to make agricultural products. These products include meat, dairy, seafood as well as other protein-rich foods required for human use. Tissue Engineering is the method employed to make animal identical products from cell cultures. To produce these cell-based products such as meat & seafood stems cells(either natural or genetically modified) are taken from a live animal and then grown in nutrient-rich conditions that promote growth. Tissue engineering is an emerging pursuit in Agri products with a previous focus on clinical applications such as organs for patients requiring organ transplantation or growing skin cells for burn victims.
Approaches Behind cellular agriculture
Two different approaches comprise cellular agriculture;
- Cellular cultivation
- Precision fermentation
Cellular cultivation is a method to produce meat & seafood by initially taking stem cells from animals through painless biopsy and then feeding them with nutrients in bioreactors where they multiply & differentiate. As they multiply and grow, they become the main component of meat called muscle tissue. Precision fermentation, another approach to cellular agriculture makes use of microbes instead of cell cultures to produce dairy products such as egg-white, soy-heme, enzymes, milk & proteins. The process of producing these products is simple as practiced before by the food industry. In this approach, DNA is taken from the source and inserted into yeast with the help of genetic engineering. Following fermentation, the product made can be used as an alternative.
Cellular Agriculture is here to replace animal farming with these advantages
Cell-based agriculture products have the potential to provide nutrient-rich food to the growing population without even worrying about owning land & natural resources. The benefits of cellular agriculture are wide-ranging as the whole process is performed is carried out in controlled environmental conditions and largely dependent on smart technologies. Compared to conventional counterparts, cellular agriculture:
- Have the least environmental impacts
- Is Reliable for consistent supply
- Provides purer & safer product
And the list of advantages is not exhausted yet! Here is another aspect of cellular agriculture that is more exciting than the above advantages. Cellular Agriculture provides you the ability to tune & design whatever you are making. For Example, If you are making meat you can make it with less saturated fats & more unsaturated fats. Another example of the advantage of this biotechnological method is that you can also design leather of different levels of thickness which was not possible earlier. With this method, you can also make milk without lactose which is an added advantage for the population that is lactose intolerant.
By Shivani Meena | June 8, 2022
BSc. (Hons) Microbiology
Alumni of Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India.